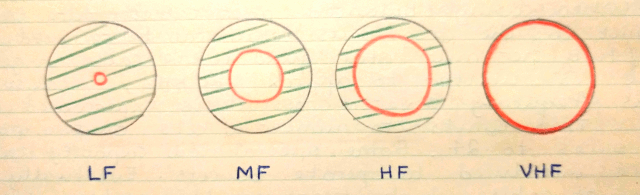
Skin Effect - Depicted above an electrical conductor cross sectional area shown on four frequency bands, LF, MF, HF and VHF. Meanwhile at low frequencies (LF) alternating current (AC) passage normally occupies the centre region of the conductor. However, as the frequency increases magnetic flux lines rise and fall more rapidly, so inducing eddy currents within the conductor. As a result the main current flow is driven out toward the conductors perimeter and finally at VHF frequencies to its surface.

Proximity Effect - When two fixed position conductors are placed side by side and close spaced the charges on them will attract one another, so drawing the charges toward each others surface.

Arranging the conductors coaxially brings together skin and proximity effects... Current on the inner most conductor flows on its outer surface whilst current flowing on the outer conductor (screen) is drawn to its inner surface... So the screening benefits of coaxial cable are complete!
